Are you curious about how much electricity your ice maker uses? You might be surprised to learn that even small appliances like ice makers can impact your energy bill.
Understanding their power consumption can help you save money and make smarter choices for your home. You’ll discover exactly how much electricity an ice maker uses and simple tips to reduce its energy use without giving up the convenience of fresh ice.
Keep reading to take control of your energy costs today!

Ice Maker Energy Basics
Understanding the energy use of an ice maker helps manage your electricity bills. Ice makers use power to freeze water and keep ice ready. Knowing how they work and their power needs can guide better energy use. This section explains the basics of ice maker energy.
How Ice Makers Work
Ice makers pull water from a supply line. They fill a mold that shapes the ice cubes. Then, a freezing system cools the water until it becomes ice. Once frozen, the ice is pushed into a storage bin. The machine repeats this cycle to keep ice ready.
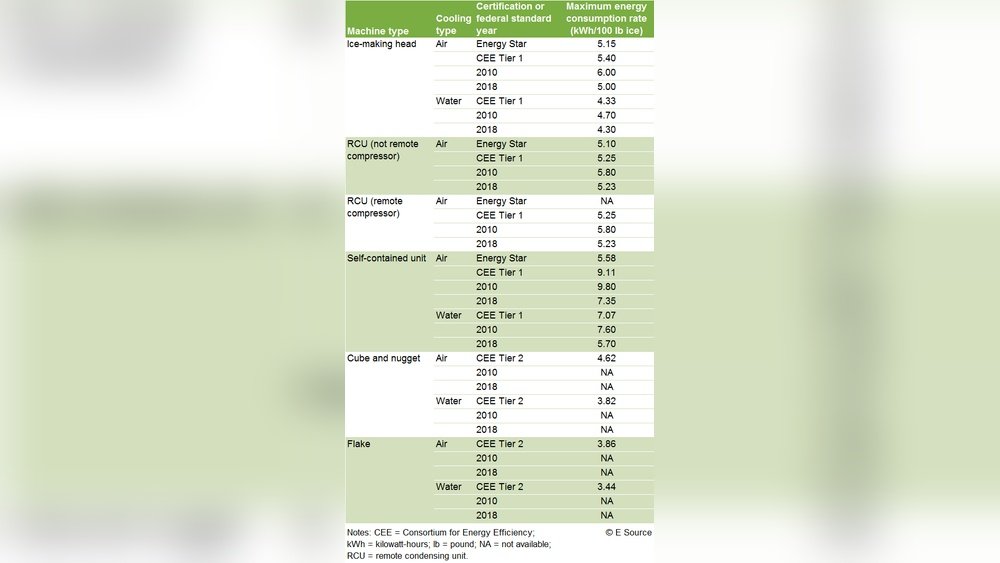
Typical Power Consumption
Most ice makers use between 100 and 300 watts while running. Power use varies by model and size. Compact ice makers use less electricity than larger, built-in ones. Running time and ice production affect total energy use. On average, an ice maker uses about 150 to 250 kWh per year.

Factors Influencing Electricity Use
Electricity use by an ice maker changes based on several factors. These factors affect how much power the machine needs daily. Understanding them helps control energy costs and improve efficiency.
Each ice maker is different. Some use more power than others. The way you use the machine also plays a role. The environment around the ice maker impacts electricity use too.
Size And Model Variations
Large ice makers use more electricity than small ones. Commercial models often consume more power than home versions. Newer models tend to be more energy-efficient. Older machines may draw more electricity to work properly.
Usage Frequency
The more you use the ice maker, the higher the electricity use. Frequent ice production means the machine runs often. This increases power consumption. Less frequent use saves electricity and lowers bills.
Environmental Conditions
Warm rooms make ice makers work harder. High temperatures cause longer freezing times. This leads to more electricity use. Cooler environments help machines run efficiently and save power.
Comparing Ice Makers With Other Appliances
Comparing the electricity use of ice makers to other home appliances helps understand their impact on energy bills. Ice makers use power to freeze water and keep ice ready. Other appliances like refrigerators and freezers also use electricity for cooling but have different energy demands. This section compares ice makers with refrigerators and freezers to show their relative electricity use.
Energy Use Vs. Refrigerators
Refrigerators use more electricity than ice makers. They run all day to keep food cold and fresh. Ice makers only work during ice production cycles. A typical refrigerator uses between 100 to 800 kWh per year. Ice makers usually consume about 100 to 200 kWh per year. This means refrigerators use about 2 to 8 times more energy than ice makers. The larger size and constant cooling raise refrigerators’ energy needs.
Energy Use Vs. Freezers
Freezers also use more energy than ice makers. They keep food frozen at very low temperatures all the time. Freezers consume around 200 to 700 kWh per year. Ice makers use less power because they only freeze small amounts of water. The continuous operation of freezers makes them less energy efficient than ice makers. Ice makers add only a small extra load to your electricity bill compared to freezers.

Tips To Reduce Ice Maker Energy Use
Reducing the energy use of your ice maker helps save money and lowers your home’s energy demand. Small steps can make a big difference in electricity consumption. These tips focus on smart placement, proper care, and choosing the right model.
Optimal Placement
Place your ice maker away from heat sources. Avoid spots near ovens, dishwashers, or direct sunlight. Heat forces the machine to work harder and use more power. Keep it in a cool, ventilated area for best results.
Regular Maintenance
Clean the ice maker regularly to keep it efficient. Remove mineral buildup and dirt from filters and trays. Check for leaks or damaged parts that waste energy. A well-maintained machine uses less electricity and lasts longer.
Energy-efficient Models
Choose ice makers with good energy ratings. Look for models labeled ENERGY STAR or similar certifications. These machines use advanced technology to reduce electricity use. Investing in an efficient model lowers your power bills over time.
Energy-saving Alternatives
Energy-saving alternatives help reduce electricity use from ice makers. They offer simple ways to enjoy ice without high power bills. Choosing these options supports a greener lifestyle and cuts down on energy waste.
Manual Ice Trays
Manual ice trays use no electricity at all. Fill them with water and place in the freezer. They take more time but save energy completely. Small and easy to store, they fit any freezer size. Perfect for those who use ice occasionally.
Portable Ice Makers
Portable ice makers use less power than built-in models. They produce ice quickly and can be moved anywhere. These devices are efficient and often use less water too. Great for small kitchens or outdoor events.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Electricity Does An Ice Maker Consume Daily?
An ice maker typically uses about 100 to 200 watts per hour. Daily consumption depends on usage frequency and model efficiency. Average daily electricity use ranges from 1 to 2 kWh, making it a low to moderate energy appliance in most homes.
Does The Ice Maker Increase My Electricity Bill Significantly?
An ice maker adds a small amount to your electricity bill. Its usage is minimal compared to larger appliances like refrigerators or air conditioners. Efficient models use less power, so the impact on monthly bills is usually minor, especially with moderate use.
How Can I Reduce Electricity Use Of My Ice Maker?
To reduce electricity use, choose energy-efficient ice makers with an Energy Star rating. Regularly clean and maintain the appliance for optimal performance. Avoid frequent opening of the ice maker, and use it only when necessary to save power and reduce waste.
What Factors Affect An Ice Maker’s Electricity Consumption?
Electricity consumption varies by ice maker type, size, and usage frequency. Features like fast ice production or built-in refrigeration increase power use. Ambient temperature and maintenance also impact efficiency. Selecting a model suited to your needs helps manage energy costs effectively.
Conclusion
An ice maker uses a small amount of electricity. It depends on the model and how often it runs. Choosing energy-efficient models can save money. Regular maintenance helps keep it working well. Knowing the electricity use helps manage your bills.
Simple steps make a big difference over time. Keep your ice maker clean and check settings. Use ice wisely to avoid waste. Small changes lead to better energy use. Understanding this helps you stay smart with power.